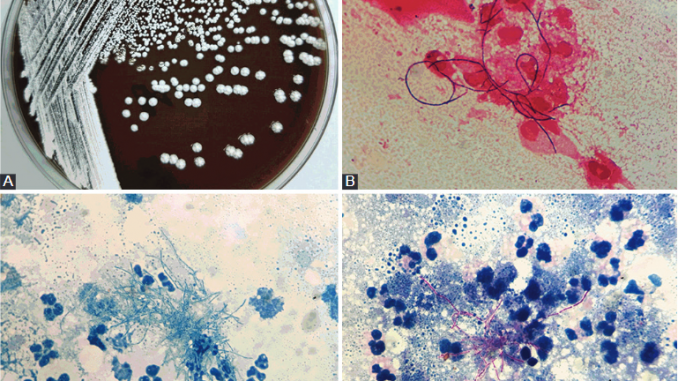
Nocardia species are classified as gram-positive, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria. As an aerobic actinomycetes, Nocardia spp. exist in a wide range of environments and have been recognized as a pathogen responsible for a variety of clinical infections. Furthermore, Nocardia spp. may cause severe, life-threatening infections. Thus, early recognition and effective therapy are imperative to achieve successful outcomes.
Meanwhile, Nocardia spp. are being distributed differently between various geographic regions. Thus, it is necessary to investigate the epidemiology, clinical characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility of Nocardia spp. in different geographic regions, especially in China, a region with widely varied geographic and climatic characteristics.
The group of researchers from Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University and Shengli Oilfield Central Hospital performed the study on Nocardia spp. and published their results in the journal BJBMS. The researchers respectively analyzed the species distribution, clinical manifestations, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Nocardia spp. in two tertiary general hospitals over 3 years in China.
As a consequence, a total of 27 Nocardia isolates were identified from 27 individuals and the researchers found that the clinical manifestations of Nocardia infection and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles were varied with diverse Nocardia species. These findings indicated that the accurate identification of these species is crucial for the diagnosis and the choice of antibiotic treatment.
Reference:
Editor: Edna Skopljak
Leave a Reply