Background
Metformin is the first-line drug for treatment of type 2 diabetes, used by over 100 million people worldwide. However, not all patients respond well to metformin. Approximately, one third of patients does not achieve acceptable glycaemic control with this medication. It has been shown that variation in glycaemic response to metformin is heritable. However, genetic factors influencing metformin response yet need to be unravelled. In this study we aimed to explore the effects of common variant rs7903146 C>T in the transcription factor 7 like 2 gene (TCF7L2) on metformin response in type 2 diabetes.
Why Was This Study Done?
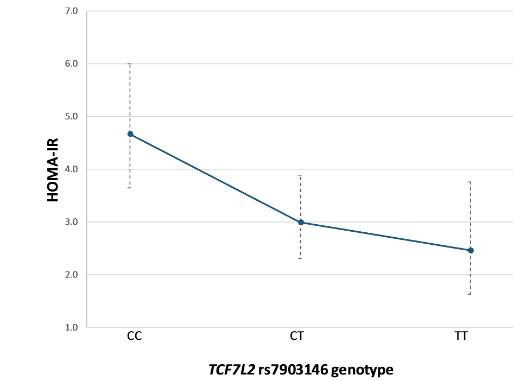
Furthermore, 86 patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, in their first year of metformin treatment, were enrolled in the study. We studied changes in levels of fasting glucose, insulin, HbA1c, total HDL-, LDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides, and anthropometric parameters. We found that patients carrying TCF7L2 rs7903146 T allele had lower fasting insulin levels and lower index of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) after 12 months of metformin therapy. Moreover, the rs7903146 T allele was also associated with a better glycaemic response to metformin assessed as fasting glucose levels after 6 months of metformin treatment.
What Did the Researchers Do and Find?
Results from our study suggest that TCF7L2 rs7903146 variant is associated with a greater decline in insulin resistance. Additionally, association was found in the better glycaemic response to metformin in newly diagnosed patients within first year of metformin treatment.
These findings contribute to explanation of high inter-individual variability in metformin therapeutic response in patients with type 2 diabetes. Unravelling of genetic factors which can influence metformin response may lead to more effective diabetes treatment.
Finally, the results of our study also add to the new insights on possible interplay between metformin and pleiotropic TCF7L2 variant. This may contribute to elucidation of still not fully understood mechanisms of action of this complex diabetes medication.
Summary in Bosnian/Croatian/Serbian language
Uvod
Metformin je lijek prvog izbora u terapiji dijabetesa tipa 2, kojeg koristi više od 100 milijuna ljudi širom svijeta. Međutim, ne reagiraju svi pacijenti dobro na lijek; otprilike jedna trećina pacijenata ne postigne odgovarajuću glikemijsku kontrolu primjenom metformina. Pokazano je da su varijacije u glikemijskom odgovoru na metformin nasljedne. Ipak, genetički faktori koji utječu na terapiju još nisu otkriveni. U ovoj studiji smo ispitali utjecaj česte varijante rs7903146 C>T gena koji kodira transkripcijski faktor TCF7L2 (TCF7L2) na odgovor na metformin kod dijabetesa tipa 2.
Zašto smo proveli ovo istraživanje?
Pratili smo promjene u nivoima natašte glukoze, inzulina, HbA1c, ukupnog, HDL-, LDL-kolesterola, i triglicerida, te antropometrijskim parametrima, kod 86 pacijenata s novootkrivenim dijabetesom tipa 2 tokom prve godine terapije metforminom. Pacijenti koji nose TCF7L2 rs7903146 T alel su imali niže nivoe inzulina natašte i niži indeks inzulinske rezistencije (HOMA-IR), nakon 12 mjeseci terapije metforminom. Osim toga, rs7903146 T alel je bio povezan s boljim glikemijskim odgovorom na metformin, mjereno kao nivo glukoze natašte nakon 6 mjeseci terapije metforminom.
Koje su metoda istraživanja i nalazi?
Rezultati naše studije ukazuju da je TCF7L2 rs7903146 varijanta povezana s većim smanjenjem inzulinske rezistencije i boljim glikemijskim odgovorom na metformin kod novotkrivenih pacijenata tokom prve godine terapije metforminom.
Ovi nalazi mogu doprinijeti objašnjenju velike interindividualne varijabilnosti u terapijskom odgovoru na metformin kod pacijenata s dijabetesom tipa 2. Otkriće genetičkih faktora koji utječu na odgovor na metformin može dovesti do efikasnijeg tretmana dijabetesa.
Naposljetku, rezultati naše studije također daju nove uvide u moguće interakcije između metformina i plejotropne varijante TCF7L2 gena. Ovo može doprinijeti rasvjetljavanju još uvijek nejasnih mehanizama djelovanja ovog kompleksnog lijeka.
Leave a Reply