Hangzhou, China – Throughout history, the medical field has been a vanguard in adopting technological advancements. Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands out as the most recent and potentially revolutionary among these innovations. A novel article, “Artificial intelligence in renal pathology: Current status and future,” penned by esteemed researchers Chunyue Feng and Fei Liu, ventures into the captivating nexus between AI and renal pathology.
The Complex World of Kidney Diseases
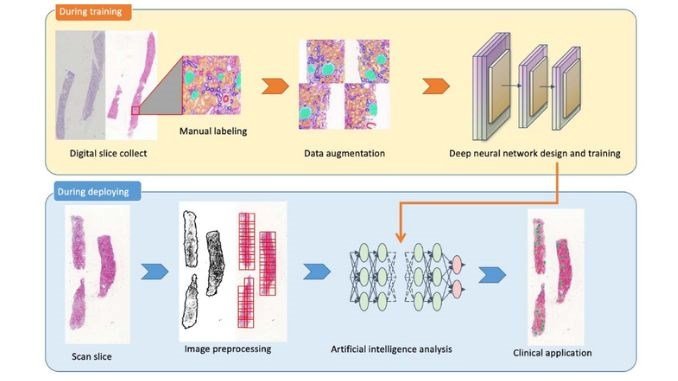
Artificial Intelligence, encapsulating subsets like deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNN), emerges as a beacon of hope in this challenging scenario. CNNs, tailored for visual analysis, have shown immense potential in examining pathology slides. Deep learning, on the other hand, can identify patterns and make predictions based on vast datasets. This research reviews the present and potential applications of AI in renal pathology, accentuating AI’s diagnostic and predictive strengths. The transformative potential of digital pathology, predictive models, and 3D imaging in renal pathology is brought to the fore.
“Our endeavor seeks to harmonize the rich legacy of renal pathology with the innovative prowess of AI. We are optimistic that AI will complement, not supplant, pathologists, setting new benchmarks in diagnostic accuracy and speed,” articulates Fei Liu, the visionary behind the study.
Embracing the AI Revolution
Artificial Intelligence, particularly the subsets of deep learning and convolutional neural networks (CNN), offers a beacon of hope. CNN, designed to analyze visual imagery, is apt for studying pathology slides. This research provides a comprehensive review of AI’s current applications in renal pathology and its promising future trajectory. The spotlight is on the diagnostic and predictive capabilities of AI, showcasing the transformative potential of digital pathology, predictive models, and 3D imaging in renal pathology.
“Our endeavor seeks to harmonize the rich legacy of renal pathology with the innovative prowess of AI. We are optimistic that AI will complement, not supplant, pathologists, setting new benchmarks in diagnostic accuracy and speed,” articulates Fei Liu, the visionary behind the study.
Discoveries in the Digital Age
The study dives deep into AI’s capabilities, highlighting its efficacy in segmenting renal cortex tissue structures. One salient discovery is the unmatched consistency when using PAS-stained Whole Slide Images (WSIs). PAS, or Periodic Acid-Schiff, is a staining technique pivotal in histology, enhancing the visibility of certain tissue structures. Merging this with AI’s analytical capabilities could potentially redefine standards in renal pathology.
The Path Forward
While AI’s promise in revolutionizing renal pathology is palpable, the journey to its seamless integration is strewn with challenges. The study highlights these potential obstacles but remains optimistic about the transformative impact AI can have on renal diagnosis.
For those unfamiliar with the term, Artificial Intelligence might seem like a futuristic concept. However, in reality, AI is an advanced branch of computer science aiming to craft machines with capabilities resembling human intelligence. Its application in medicine has been vast, ranging from robotic surgeries to drug discovery. In the context of renal pathology, AI excels at analyzing pathology slides, capturing nuances that might be overlooked by the human eye.
The research methodology adopted was a narrative review, exploring the myriad AI applications in renal pathology. The study not only focused on diagnostic capabilities but also delved into AI’s potential in predictive and prognostic applications, offering a comprehensive understanding of its role in renal pathology images, 3D imaging, and predictive modeling.
Considering the challenges in renal pathology, AI’s role is indeed pivotal, providing a solution to the expertise gap and addressing the rising prevalence of kidney diseases. Dr. Fei Liu, reflecting on the findings, remarked, “In an era where technology is reshaping every facet of our lives, healthcare is no exception. Our exploration into combining AI with renal pathology signals the dawn of numerous advancements. Collaborative efforts will undoubtedly usher in a transformative era in kidney disease diagnosis.”
The translation of the preceding English text in Chinese:
杭州,中国 – 纵观历史,医学领域一直是采纳技术进步的先锋。人工智能(AI)被视为这些创新中最新且可能最具革命性的。由尊敬的研究者冯春月和刘飞所撰写的一篇新文章 “人工智能在肾脏病理学中的当前状态和未来” 探讨了AI和肾病理学之间引人入胜的关系。
肾脏疾病的复杂世界
人工智能,包括深度学习和卷积神经网络(CNN)等子集,在这一具有挑战性的场景中显现为希望的灯塔。为视觉分析量身定制的CNN在检查病理学幻灯片方面显示出巨大的潜力。另一方面,深度学习可以根据大量数据集识别模式并进行预测。这项研究回顾了AI在肾病理学中的当前和潜在应用,强调了AI的诊断和预测能力。数字病理学、预测模型和肾病理学中的3D成像的变革潜力被突显出来。
刘飞,这项研究背后的远见者,阐述说:”我们的努力旨在使肾脏病理学的丰富遗产与AI的创新实力相协调。我们乐观地认为,AI将补充而不是取代病理学家,为诊断的准确性和速度设定新的基准。”
数字时代的发现
该研究深入探讨了AI的能力,强调了其在分割肾皮质组织结构方面的功效。一个显著的发现是使用PAS染色的整张幻灯片(WSIs)时所达到的无与伦比的一致性。PAS,或称为周期酸- Schiff,是一种在组织学中至关重要的染色技术,增强了某些组织结构的可见性。与AI的分析能力结合可能会重新定义肾脏病理学的标准。
前进之路
尽管AI在革命化肾病理学方面的承诺是显而易见的,但其无缝集成的旅程充满了挑战。该研究突出了这些潜在的障碍,但对AI对肾脏诊断的变革影响保持乐观态度。
对于那些不熟悉这个术语的人,人工智能可能看起来像一个未来主义的概念。然而,实际上,AI是计算机科学的一个先进分支,旨在制造出具有类似于人类智能的功能的机器。其在医学中的应用范围很广,从机器人手术到药物发现。在肾病理学的背景下,AI擅长分析病理学幻灯片,捕捉可能被人眼忽略的细微差别。
采用的研究方法是叙述性回顾,探索了肾病理学中AI应用的广泛范围。该研究不仅关注了诊断能力,还深入探讨了AI在预测和预后应用中的潜力,提供了对其在肾病理学图像、3D成像和预测建模中的作用的全面理解。
考虑到肾脏病理学中的挑战,AI的角色确实是关键的,提供了一种解决方案,弥补了专家知识的差距,并解决了肾脏疾病的日益增长的流行病学问题。刘飞博士在反思这些发现时评论说:”在技术正在重塑我们生活的每一个方面的 时代,医疗保健无疑是重要的受益者。我们将AI与肾病理学结合的探索仅仅是开始。通过跨学科的合作努力,我们有望开启肾脏疾病诊断的变革时代。”
Reference: Feng C, Liu F. Artificial intelligence in renal pathology: Current status and future. Biomol Biomed [Internet]. 2023Mar.16 [cited 2023Oct.6];23(2):225–234. Available from: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/8318
Editor: Ermina Vukalic
Leave a Reply