Stroke is not only one of the three leading causes of death in humans, but also a common cause of chronic disability in adults. The pathogenesis of the stroke is quite variable. However, the genetic factors play an important role in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke. Furthermore, epigenetic modifications provide a new direction to study the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke.
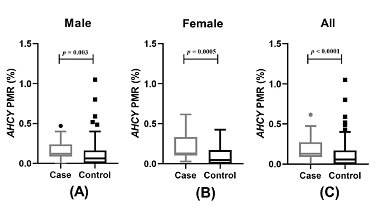
Recently, the group of researchers from Zhejiang University School of Medicine, performed a case-control study to determine the correlation between the DNA methylation in S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (AHCY) and the risk of ischemic stroke.
In their paper, published in the journal BJBMS, they confirmed that the DNA methylation levels of AHCY were significantly associated with the risk of ischemic stroke. Hence, AHCY methylation could be used as a potential marker for the diagnosis of ischemic stroke. However, further evaluations with a larger sample size need to elucidate the relationship between AHCY gene methylation levels and ischemic stroke in multiple ethnic populations.
Reference:
Zhao L, Chen X, Zhou S, Lin Z, Yu X, Huang Y. DNA methylation of AHCY may increase the risk of ischemic stroke. Bosn J of Basic Med Sci. 2020
Editor: Edna Skopljak
Leave a Reply