Neonatal sepsis (NS) occurs in neonates within 28 days of birth, and the current diagnostic biomarkers are unsatisfactory as a result of their poor specificity. During the past decades, a series of differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) have been detected in various human diseases, and their clinical role in disease diagnosis and prognosis attracts more and more attention.
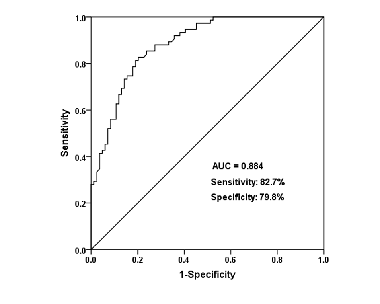
The study published in BJBMS investigated the clinical value of miR-129-5p in neonatal sepsis. The authors studied its role in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory response in monocytes. A total of 75 patients with neonatal sepsis and 84 neonates with respiratory infection or pneumonia were recruited. LPS treated monocytes were used for cell experiments. The authors found that miR-129-5p was low expressed in the serum of patients with neonatal sepsis, as compared with controls. Furthermore, the ROC curve suggested its diagnostic value for neonatal sepsis.
In patients with neonatal sepsis, serum miR-129-5p level was closely associated with TNF-α and IL-8 levels. In vitro, overexpression of miR-129-5p inhibited the release of inflammatory cytokines in LPS treated monocytes. The authors concluded that the dysregulation of miR-129-5p might be a promising biomarker for disease diagnosis, and the overexpression of miR-129-5p alleviated the inflammatory response of neonatal sepsis.
However, the results of animal studies were not included in this study, which could be beneficial to verify the study results. Additionally, the underlying mechanism of the role of miR-129-5p in neonatal sepsis should be further investigated in future studies. These results provide a theoretical basis for the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal sepsis.
References:
Editor: Edna Skopljak, MD
Leave a Reply