A study titled “Advances in Nanotechnology-Enabled Drug Delivery for Combining PARP Inhibitors and Immunotherapy in Advanced Ovarian Cancer” meticulously explores the utilization of a nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery system to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of combining poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors with immunotherapy for treating advanced ovarian cancer. Authored by Lama Abujamous, Abderrezzaq Soltani, Hamda Al-Thawadi, and Abdelali Agouni from Qatar University, this review study examines the current landscape of treatment for advanced ovarian cancer, emphasizing the challenges of drug resistance and the promising approach of combination therapy facilitated by nanotechnology.
Ovarian cancer, often dubbed the “silent killer” due to its late diagnosis, is a leading cause of mortality among women worldwide. Despite available treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, advanced therapeutic strategies such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy are being explored due to the persistence of drug resistance. Nanotechnology emerges as a valuable alternative, enhancing drug delivery precision and minimizing toxicity.
Human Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer’s high mortality rate is attributed to its late diagnosis, with symptoms that are often nonspecific. Its pathogenesis is linked to various risk factors, including genetic predispositions and environmental influences. The complexity of ovarian cancer’s pathophysiology, impacting different cell types, underscores the challenge in treatment and prognosis.
The first-line treatment involves surgery and chemotherapy. However, drug resistance remains a significant hurdle, highlighting the need for a broader array of treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes. Targeted therapy, including the use of PARP inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), presents a promising approach.
PARP Inhibitors in the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
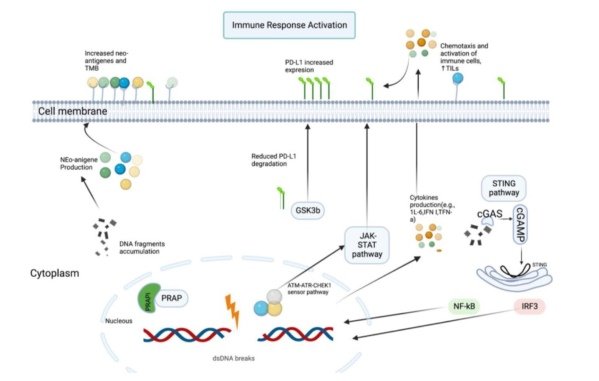
PARP inhibitors target DNA repair mechanisms, offering a novel treatment strategy for advanced ovarian cancer. The challenge of resistance and relapse after initial therapy with PARP inhibitors necessitates exploring innovative approaches, including combination therapies with ICIs, to manage advanced ovarian cancer effectively.
Immunotherapy, particularly with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has revolutionized cancer treatment. However, its efficacy varies across different cancer types. Combination therapies with ICIs and other anticancer agents, such as PARP inhibitors, show promise in treating ovarian cancer, reflecting in findings from several clinical trials.
Combining PARP inhibitors with ICIs aims to overcome resistance and enhance efficacy. This synergy has shown great promise in advanced ovarian cancer treatment, as evidenced by clinical trials demonstrating higher response rates and progression-free survival.
Challenges in Drug Delivery for Combining PARP Inhibitors and ICIs
Targeted molecular therapies for ovarian cancer face challenges like resistance and severe side effects. Targeted delivery systems, such as nanocarriers, offer a solution by enhancing therapeutic selectivity, overcoming drug resistance, and minimizing systemic toxicity.
The complexity of treating ovarian cancer underscores the importance of innovative treatment strategies, such as combining PARP inhibitors with ICIs, facilitated by nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery. The potential of nanoparticles in targeted therapy holds promise for improving cancer treatment efficacy beyond traditional chemotherapy, indicating a significant shift towards more personalized and effective cancer management strategies.
The translation of the preceding English text in Arabic:
دراسة بعنوان “تقدم في توصيل الأدوية بتقنية النانو لدمج مثبطات بولي (أدينوزين ثنائي الفوسفات-ريبوز) بوليميراز (PARP) والعلاج المناعي في سرطان المبيض المتقدم” تستكشف بدقة استخدام نظام توصيل الأدوية المدعوم بتقنية النانو لتحسين فعالية العلاج بدمج مثبطات بولي (أدينوزين ثنائي الفوسفات-ريبوز) بوليميراز (PARP) مع العلاج المناعي لعلاج سرطان المبيض المتقدم. من تأليف لمى أبو جاموس، عبد الرزاق سلطاني، حمدة الثوادي، وعبد العلي أغوني من جامعة قطر، تقوم هذه المراجعة الأدبية بفحص المشهد الحالي لعلاج سرطان المبيض المتقدم، مع التركيز على تحديات مقاومة الأدوية والنهج الواعد للعلاج المركب الذي يسهله تقنية النانو.
سرطان المبيض، والذي غالبًا ما يُطلق عليه “القاتل الصامت” بسبب تشخيصه المتأخر، هو سبب رئيسي للوفاة بين النساء على مستوى العالم. على الرغم من وجود علاجات متاحة مثل الجراحة والعلاج الكيميائي والإشعاعي، فإن استراتيجيات العلاج المتقدمة مثل العلاج الموجه والعلاج المناعي يتم استكشافها بسبب استمرار مقاومة الأدوية. تظهر تقنية النانو كبديل قيم، تعزز من دقة توصيل الأدوية وتقلل من السمية.
سرطان المبيض البشري
يُعزى معدل الوفيات العالي لسرطان المبيض إلى تشخيصه المتأخر، مع أعراض غالبًا ما تكون غير محددة. يرتبط تكوين سرطان المبيض بعوامل خطر متنوعة، بما في ذلك الاستعدادات الجينية والتأثيرات البيئية. تعقيد فيزيولوجيا سرطان المبيض، الذي يؤثر على أنواع مختلفة من الخلايا، يبرز التحدي في العلاج والتشخيص.
العلاج الأولي يتضمن الجراحة والعلاج الكيميائي. ومع ذلك، تظل مقاومة الأدوية عقبة كبيرة، مما يبرز الحاجة إلى مجموعة أوسع من استراتيجيات العلاج لتحسين نتائج المرضى. يقدم العلاج الموجه، بما في
ذلك استخدام مثبطات PARP ومثبطات نقاط التحكم المناعي (ICIs)، نهجًا واعدًا.
مثبطات PARP في علاج سرطان المبيض
تستهدف مثبطات PARP آليات إصلاح الحمض النووي، وتقدم استراتيجية علاجية جديدة لسرطان المبيض المتقدم. تحدي المقاومة والانتكاس بعد العلاج الأولي بمثبطات PARP يستدعي استكشاف نهج مبتكرة، بما في ذلك العلاجات المركبة مع ICIs، لإدارة سرطان المبيض المتقدم بفعالية.
العلاج المناعي، وخاصة مع مثبطات نقاط التحكم المناعي (ICIs)، قد ثور في علاج السرطان. ومع ذلك، تختلف فعاليتها عبر أنواع السرطان المختلفة. تظهر العلاجات المركبة مع ICIs ووكلاء مضادات السرطان الأخرى، مثل مثبطات PARP، وعدًا في علاج سرطان المبيض، كما يتضح في نتائج عدة تجارب سريرية.
دمج مثبطات PARP مع ICIs يهدف إلى التغلب على المقاومة وتعزيز الفعالية. أظهر هذا التآزر وعدًا كبيرًا في علاج سرطان المبيض المتقدم، كما يتضح من التجارب السريرية التي أظهرت معدلات استجابة أعلى وبقاء خالي من التقدم.
التحديات في توصيل الأدوية لدمج مثبطات PARP و ICIs
تواجه العلاجات الجزيئية المستهدفة لسرطان المبيض تحديات مثل المقاومة والآثار الجانبية الشديدة. تقدم أنظمة التوصيل المستهدفة، مثل الناقلات النانوية، حلاً من خلال تعزيز الانتقائية العلاجية، التغلب على مقاومة الأدوية، وتقليل السمية الجهازية.
تعقيد علاج سرطان المبيض يبرز أهمية استراتيجيات العلاج المبتكرة، مثل دمج مثبطات PARP مع ICIs، التي يسهلها توصيل الأدوية بتقنية النانو. إمكانات الجسيمات النانوية في العلاج المستهدف تعد بتحسين فعالية علاج السرطان مقارنة بالعلاج الكيميائي التقليدي، مما يشير إلى تحول كبير نحو استراتيجيات إدارة السرطان الأكثر شخصية وفعالية.
Reference: Abujamous L, Soltani A, Al-Thawadi H, Agouni A. Advances in nanotechnology-enabled drug delivery for combining PARP inhibitors and immunotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer. Biomol Biomed [Internet]. 2023 Nov. 23 [cited 2024 Feb. 9];. Available from: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/9757
Editor: Ermina Vukalic
Leave a Reply