post
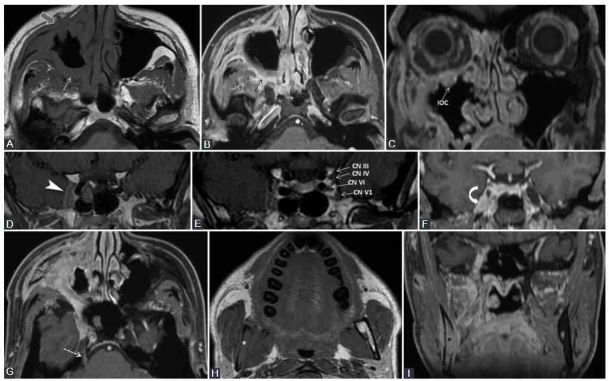
A 39-year-old male diagnosed with adenoid cystic carcinoma of maxillary sinus, with multiple extensions. Clinically: Right abducens nerve palsy, diplopia, right infraorbital anesthesia. Axial T1-weighted (A, H), axial (B, G), and coronal (C, F, I) con-trast-enhanced (CE) 3D T1 FSPGR; coronal contrast enhanced in Phase T1 FSE IDEAL (D, E) images. The probable first point of PNS is PPF with fat obliteration (white arrow) and CE (black arrow), where the V2 nerve is involved. In an anterograde direction, the tumor reaches the right infraorbital nerve, demonstrated by infraorbital canal enlargement with CE (IOC) and preantral fat obliteration (gray arrow). Following the main V2 trunk, the tumor reaches the cavernous sinus which appears larger and shows CE (arrowhead). Note that in CN III, IV, V1, and V2 are situated in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, the cavernous segment of CN VI is located medially to the CN V1, implying the tumoral involvement of the mentioned nerves. There is Meckel’s cave CE (curved arrow) and the tumor traveled back up to the main trigeminal trunk (cisternal segment, dashed arrow). Notice the right mandibu-lar fat replacement (white *), associated with mandibular CE (black *), and cortical disruption, meaning an anterograde PNS from the Meckel’s cave to the inferior alveolar nerve (branch of V3). Olga Medvedev, et al.: Perineural spread in head-and-neck malignancies
Leave a Reply