Researches indicated that gastric cancer is the fifth most prevalent cancer globally and has the third-highest mortality rate among all cancers. Thus, it is imperative to explore biomarkers to assess patients’ prognoses and provide possible assistance in clinical management.
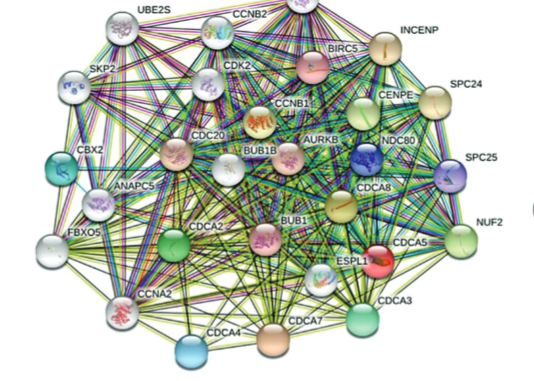
In the study published in BJBMS, Cell Division Cycle Associated (CDCA) proteins were investigated with different bioinformatic tools because they are closely related to the cell cycle, which is critical in tumor development. Furthermore, the authors concluded that CDCAs serve as potential prognosis-associated biomarkers for gastric cancer.
The researchers found that all CDCAs were higher expressed in cancer tissues, and high levels of CDCA4, 7, and 8 were linked with worse outcomes. The gene mutations of CDCA1, 3, 4, and 8 were predicted to damage the protein functions, which might be adverse to the prognosis.
CDCA proteins were shown to inhibit the immunocyte infiltration, thus causing poorer outcomes due to the anti-cancer effects of several immunocytes. These findings indicated that targeted CDCAs treatment might be effective for gastric cancer management. However, further basic and clinical experiments are needed to validate the findings and explore the underlying mechanisms.
This study might offer additional assistance for clinicians to detect CDCAs levels in early gastric cancer screening, use CDCAs levels as a reference basis in the treatment process, or design immune drugs targeting CDCAs, thus improving the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer.
Reference:
Lu P, Cheng W, Fang K, Yu B. Multidimensional study of cell division cycle-associated proteins with prognostic value in gastric carcinoma. Bosn J of Basic Med Sci 2021. Available from: https://www.bjbms.org/ojs/index.php/bjbms/article/view/5783
Editor: Edna Skopljak, MD
Leave a Reply