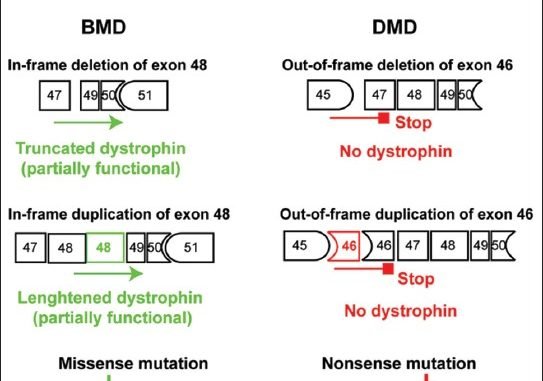
Mutations of the dystrophin DMD gene, essentially deletions of one or several exons, are the cause of two devastating and to date incurable diseases, Duchenne (DMD) and Becker (BMD) muscular dystrophies. Depending upon the preservation or not of the reading frame, dystrophin is completely absent in DMD, or present in either a mutated or a truncated form in BMD. DMD is a severe disease which leads to a premature death of the patients. Therapy approaches are evolving with the aim to transform the severe DMD in the BMD form of the disease by restoring the expression of a mutated or truncated dystrophin. These therapies are based on the assumption that BMD is a mild disease. However, this is not completely true as BMD patients are more or less severely affected and no molecular basis of this heterogeneity of the BMD form of the disease is yet understood. The aim of this review is to report for the correlation between dystrophin structures in BMD deletions in view of this heterogeneity and to emphasize that examining BMD patients in details is highly relevant to anticipate for DMD therapy effects.
This article was published as:
Elisabeth Le Rumeur. Dystrophin and the two related genetic diseases, Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Aug; 15(3): 14–20. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2015.636
Leave a Reply