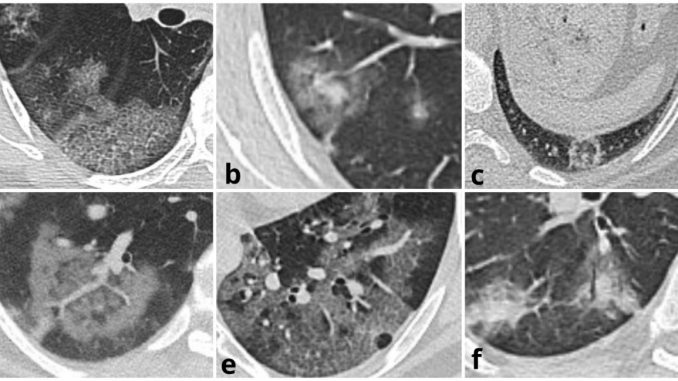
The COVID-19 disease has been declared a pandemic, when disease with pneumonia, whose definitive treatment has not yet been found, spread around the world in December 2019. More than one hundred million cases and more than two million deaths have been reported as of February 2021. Although PCR is the definitive method at the diagnosis stage, CT has become an important tool in the management of patients in combating the pandemic. In previous studies, the diagnostic performance of CT and scoring systems to predict poor prognosis were studied. In the study published in BJBMS, the authors aimed to compare the scoring systems of CT and the compatibility between the observers evaluating CT.
In this study, data of 405 patients from two tertiary university hospitals were analyzed. The results of the present study published in BJBMS, the rate of Zonal CT Visual Score at the first admission may predict the subsequent requirement of ICU admission. Patients with a ZCVS of 20 had a 20% possibility of going to the intensive care unit. In contrast, in patients with a score of 45, this rate was above 80%, regardless of clinical and demographic parameters.
Moreover, the prognostic nomogram we have created can provide an estimate of the probability of adverse outcome. These estimates facilitate the clinician’s decision for respiratory support in the rush of the pandemic.
Leave a Reply