Numerous studies have shown that patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and atherosclerosis are subject to chronic, mild, subclinical inflammation. Furthermore, these studies have shown the that inflammation plays an important role in the development of atherosclerosis and complications in the patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus.
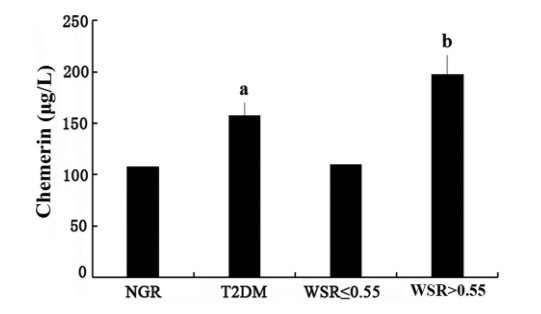
To date, the development of macroangiopathy related to type-2 diabetes mellitus is widely accepted to be subject to chronic inflammatory reactions, in essence. Moreover, variety of inflammatory factors participate in this process. Chemerin plays a role in both inflammation and metabolism, and thus may provide a link between chronic inflammation and obesity and its related disorders.
The group of researchers from Zunyi Medical University and Ningbo No. 2 Hospital studied the serum chemerin levels in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. In their study published in BJBMS, the researchers analyzed the serum chemerin levels in these patients, with and without lower extremity macroangiopathy and the correlation between the serum chemerin levels and body fat, glucolipid metabolism, and insulin resistance (IR).
They concluded that the chemerin may be associated with obesity, pathological and physiological changes in glucolipid metabolism and inflammatory factors. Furthermore, they found that chemerin may promote the development of macroangiopathy in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus.
Reference:
Editor: Edna Skopljak
Leave a Reply